Category Archives: Knowledge
05 Jun Intelligent Traveling Salesmen

Another Sample Problem Several specific reasoning or inference problems have provided fodder for AI textbooks and experiments. One of these is the traveling salesman problem (Get an explanation and an example applet here): Given a traveling salesman who must get to x number of cities, find the shortest route the salesman can travel to reach […]
03 Jun Distributed Knowledge Representation

Distributed KR Knowledge representation schemata may be top-down, or bottom-up. In a top-down approach, one would define an area or domain of knowledge, then list the concepts within the domain and their attributes. Behaviors within the domain are often defined by that domain, and the concepts may not be able to exist independently. This approach helps enforce a […]
02 Jun Framing Formal Logic
Formal Logic Formal logic often uses set theory. Set theory uses existential (an assertion that something applies to some members of a set) and universal (a statement that applies to all members in a set) quantifiers. Despite the utility and noncommittal correctness of existential quantifiers, set operations using existential quantifiers are weaker then those using universal quantifiers. The […]
28 May Data and Modeling
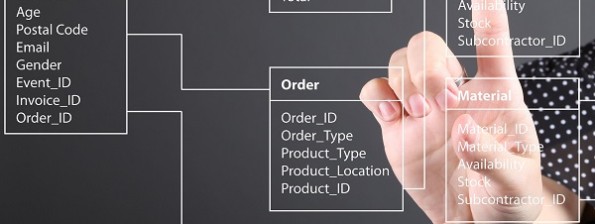
Data modeling is essential in the early stages of any information system design. By moving toward a data-centered model, we can make our data, and our system, smarter. There are many data-modeling techniques, but we will focus on two for now: Entity Relationship Diagramming (ERD), and Object Role Modeling or object relational modeling (ORM). Entity […]
27 May Machine Components for Intelligence
If an abacus or a log and rope can be considered intelligent machines, then we can decompose their parts, possibly rearrange them, and get different kinds of intelligent machines. I know this is an extreme example of absurd reasoning. Let’s go from the opposite direction in the complexity spectrum. Can we use the human brain and its parts as […]
26 May AI Domains and Approaches

Grouping, Classifying and Categorizing How do you solve big technical problems? Rather than selecting or inventing an approach and then attempting to apply it to a problem to see how well it works, let’s analyze the problem and see if we can find or invent a solution that matches the problem space, and see if […]
20 May Cybernetic Modeling for Smarty-Pants

Introduction Model railroads come in several scales: O, HO and N gauge enable hobbyists to model real-world objects in miniature using successively smaller standards. In N gauge it is possible to build an entire city in the basement. A good model photographed with still or motion pictures may be so realistic that viewers believe they are looking […]
19 May Deixis and Context

Deixis, is a common type of ambiguity that is mediated at the level of context. When deixis occurs in written language, you can normally resolve questions about the identity of the person(s) referenced in the ‘he’, ‘she’ or ‘they’ pronoun. In speaking, you sometimes have to ask the person who said it. 3-DG places context in […]






