Category Archives: Cognitive Science
09 May Stratum Morphology

Morphology Morphology is about what happens to words to change their structure, impacting their meaning and usage. In English, we add -s or -es at the end of words to make them plural (guy –> guys, time –> times). Japanese, on the other hand, uses reduplication (hito –>hitobito, toki –> tokidoki) to make words plural. Adding to words, affixation, has three […]
08 May Three-Dimensional Model of Language
Topographical maps of concepts in a text provide useful views of language. Fortuna et al in Semantic Knowledge Management (pp. 155-169) describe how three-dimensional topic maps can both give meaningful insights into clusters of related content, such as news stories or published papers. I have frequently stressed the importance of concept associations in the brain, in cognitive […]
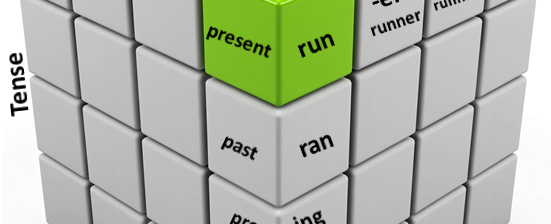
07 May Pairs of Language Strata

The Paired Model By pairing language strata, we attempt to find or describe symmetrical structures in language, thus helping clarify one of the most abstract phenomena known to man: verbal communication. This pairing of characteristics is also useful in decomposing the problem into smaller chunks to make it easier for computers to deal with. A note […]
06 May Impulse Waves in Layers

Layered Model Just as the brain has areas with three to six distinct layers, a typical artificial neural systems (ANS) also has several layers. The example at right shows a network with three layers that illustrate a neural network‘s distributed architecture. The uniform circles connected by lines are symbolic of the state of an ANS at […]
05 May Learning from Errors

If at first you don’t succeed, try – try again. Humans are pretty good at learning from our mistakes. In fact, some suggest that whatever doesn’t kill you makes you stronger. Today I’d like to riff on that theme a bit, and talk about ways in which machines can implement learning from errors. Error Minimization […]









