25 Oct Chaos and Order, Fractals and Language Power

Fractals may appear chaotic when viewed from a distance, but they exhibit recognizable patterns or mirrored structures when viewed up close. So, too, there is a distance we humans must travel from the chaotic structure of a thought to the regular structure of a meaningful dialog made of symbols in the form of audible words and body language. […]
31 Mar Asymmetrical Balance, True Love and Chaos

Inequality is the Pattern Unequal distributions characterize everything in the universe from subatomic particles to galaxies. In fact the whole idea of “equality” in the physical universe seems at least a tiny bit sketchy. At the extreme end of unequal distributions is chaos. On the near end are things that approximate equality: balance, parity, equal opportunity, symmetry […]
26 Feb Choosing an Ontology Framework
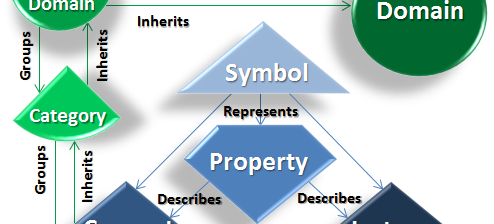
Ontology is a knowledge representation language like Roger Schank‘s Semantic Networks and John Sowa‘s Conceptual Graphs or Doug Lenat‘s Semantic Web. An Ontology framework is the model (structure, function and content definition) in which you choose to build your ontology. Like a Relational Database or an Object Oriented Programming Language, an ontology has defined structures, functions […]
24 Feb Intro to the End of Code

By: Joe Roushar – February 2013 In the Beginning When computer programming began, it consisted mostly of written computer instructions called code. Data was minimal. Decks of dozens to hundreds of punched cards told the computer what to do with the data, which was also encoded on punched cards. The process of writing and debugging code was tremendously tedious. As computing […]
07 Dec Probability of Understanding Meaning
Some suggest that computers can achieve full language understanding capabilities using statistical models. Others argue that heuristics or programmatic interpretation that uses special procedures tailored to linguistic phenomena. The two camps are as far apart as ever. Consider the comments around this recent article on Tor.com. On the one side, Norvig demonstrates the validity […]
03 Dec Language Expressiveness

Expressiveness Human languages are eloquent vehicles for giving form to the motion of the human mind. They provide symbol-rich expressions for our thoughts and communications. Language is dynamic and defies circumscription. Yet, it is circumspect; it is also useful and extremely beautiful. To comprehend is to begin to capture that beauty. The expressiveness of language […]
05 Nov Evolution of Language

Evolution of Language Did humans become smart by necessity? With the forces of nature combined to rig the test for “survival of the fittest”, as human evolution from lower forms, how did these ill-equipped creatures, with their weak jaws and thin hides, make the natural-selection cut? It sounds like it was a perilous journey. One […]






