Category Archives: Social Interaction
09 Oct Resolving a Paradox
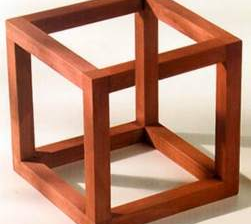
In time and space some things are impossible, but the pen is more powerful than reality. I can draw a world in which stairs lead in crazy, mind-bending directions, and I could probably build a structure that implemented upside-down staircases to nowhere. But I could never build the cube shown here, because it violates some […]
08 Aug The Fourth Dimension

To everything, turn, turn, turn, there is a season… Time is a fundamental and omnipresent element of context. It goes intrinsically with space, so much so, that we sometimes hear about a “time-space continuum” in which all things occur. Space and time are relevant to brain processes: electrical potential moves through physical pathways and brain […]
22 Jul Context Collapse: Communication Without Boundaries

In social media, “Context is everything” – says Danna Boyd. And although she is completely correct, the picture is much larger than just social media. In all media, and all communication, context is essential to understanding (Video). Los Angeles Clippers Owner, Donald Sterling was stung and surprised by the fact that his recorded statements indicted him as […]
26 Jun The Semantic Web and Model Owls

Standards protect us and constrain us — not like a straight-jacket protects us from ourselves, but more like a governor on the motor protects us from going crazy. Standards organizations such as the Worldwide Web Consortium (W3C) are there to coordinate between stakeholders to develop a common way of structuring things. The Object Management Group (OMG) is a […]
07 Jun Finding a Tree in the Forest

Complex Search Finding the information you need can be a problem, particularly when you have to look through tons (or terabytes) of data. I recall when geocaching first became popular. The idea that a technology could create a model for an entertaining activity that connects people in unusual ways is quite diverting. Will it still be popular […]
30 May State of the Art in Knowledge Representation

KR Evolves Slowly The state of the art in computer programming has evolved toward data-driven techniques. In early programs, the data was “hard-coded” into the program with specific functions operating differently on each data item and type. Gradually, programmers began storing data and templates in different files, attempting to write orthogonal procedures to introduce a modularity […]
22 May What Constitutes a Brain

By: Joe Roushar – May 2014 Mechanical Brains In its most general sense, the term mechanical brain could be applied to any man-made contrivance that is capable of functioning or generating information in some manner analogous to thinking. Under this broad definition, if the function were remembering an image (as we remember people’s faces), a camera with […]
05 May A Slice of Language

A Different Approach The previous section explained why we need the ground-up formulation of a new grammar for Natural Language (NL) understanding: none of the existing ones can accommodate the high demands of modern technology and approximate the paradigm of artificial intelligence as a model for human linguistic competence and performance across all linguistic phenomena. In […]
03 May Up from Words to Sentences

Words and Sentences The game of Scrabble is completely about words. Crossword puzzles go from sentence or phrase to word. Our analytical approach begins with the word, but doesn’t stop there. From both the cognitive and computational perspectives, the sentence exhibits far more complexity and changeability than the word. At any given moment, the structure of […]
02 May Linguistic Building Blocks

Linguistic Building Blocks While languages are infinite, each has a finite number of structures, functions and attributes. Functions and attributes are the building blocks of a grammar. Grammars or languages are categorized as regular, context-free (CF), context-sensitive (CS), recursive, and recursively enumerable. A context-sensitive grammar is a powerful formalism that describes the language in terms of […]




