Tag Archives: context
21 Oct Fuzzy Interconnectedness

Fuzzy and Interconnected Techniques Section 5 suggests that the software of cognition is very fuzzy and able to operate efficiently even without having complete or totally accurate information. We said that we want to replicate that flexibility. We spoke in Section 7 about different fuzzy approaches for representing and processing information. These approaches include artificial […]
17 Oct Neural Conceptual Dependency
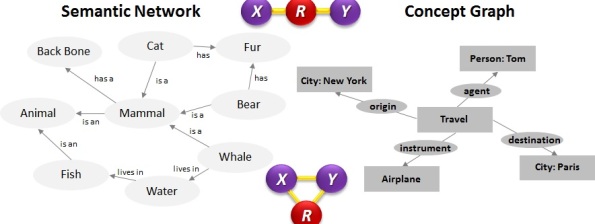
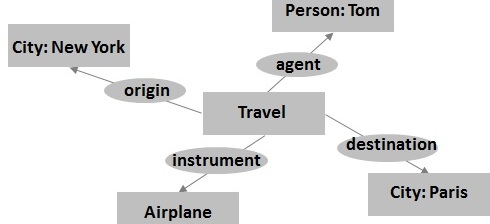
Conceptual Dependency Much of this blog has been about knowledge representation: how the brain might learn and process it, how cognitive functions treat knowledge, and now, how computers may store and process it. Conceptual structures and conceptual dependency theories for computation have been useful for categorizing and representing knowledge in intuitively simple and cognitively consistent […]
14 Oct Knowledge in Non-Neural Models
Non-Neural Models So far we have examined a number of models that are explicitly designed to be neuromorphic. This categorization is useful for two reasons: the apparent chaos or non-deterministic functioning of the brain is represented by these models; and neural networks explicitly use large numbers of distributed processors or neurodes that each contribute to […]
08 Sep Gnostic Learning Model
In prior posts in this section, and periodically in other sections of my blog, I have been exploring how humans learn, and how we might replicate those processes in computer software or (less likely) hardware. The context of the learning, or knowledge acquisition, upon which I choose to focus is language learning. While knowledge acquisition is much broader, this is an […]
25 Aug Determinacy in Neural Connections
For many years, researchers thought that it was wrong to assume that there was a cell or set of cells in the brain that stored the memory of Grandma’s face. Though the comparison with computer memory was appealing, it was thought to be too simplistic and incorrect. Now, more researchers in different academic disciplines are assuming […]
02 Aug Artificial Time

Time is omnipresent – you can’t get away from it. It is woven into everything we do and say and understand. It is an inextricable element of context. I was just speaking of how the connections in our brain develop, grow and evolve over time. Representing and handling this “temporal” element is fundamental to any […]
31 Jul Modeling Non-Random Synaptic Links

I have discussed the different meanings of “random” in “The Random Hamlet” and “That’s so Random!” in which the mathematical definition presumes there is some not yet known law that governs the phenomenon, where other definitions suggest that randomness means that the phenomenon is not governed by any law. Remember our reference to Rosenblatt’s early contributions in […]
28 Jul Patterns in the Mind

As we look for suitable solution designs for representing the knowledge and processes we humans use to communicate, we realize that we have no idea what knowledge in the brain looks like. Further, we only have relatively vague ideas about the processes that occur in the brain as we produce and comprehend words, phrases and sentences. […]