Category Archives: Cognitive Science
16 Jan Roots of Neural Nets
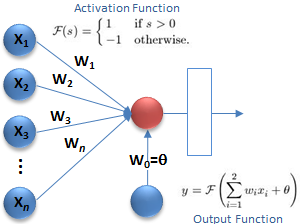
Roots of Neural Nets The concept of the modern Artificial Neural Systems (ANS) has its roots in the work of psychologists and philosophers as well as computer scientists. As mentioned in prior posts, Aristotelian theories on cognition and logic influenced the development of automata theory and associationism, spawning connectionism or parallel distributed processing (PDP) theory. Connectionism is the […]
14 Jan Visual Input Processing
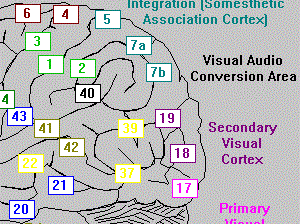
The visual cortex in the human brain is arguably the pattern after which most artificial neural networks were modeled: the flow of signals is directional through layers 1, 2 then 3; and large numbers of the cells are touched by the flow of action potentials through the system. The variations in the cells, however, contrasts with the artificial […]
13 Jan Harmonic Convergence of Light
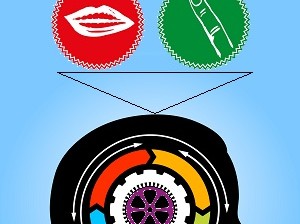
Light waves diverge and converge and bend on their journey to places where they are perceived. We choose to focus, perceived light waves enter us through the portals of our eyes, then flow through the visual cortex and resonate in the brain until they trigger recognition, often very quickly. The illustration shows a lens that […]
10 Jan Shades of Meaning

I have been sharing my observations on the electrical behavior of the brain this month, with a brief glance at perspectives on perception. My work began, and may end with language. As my springboard into artificial intelligence, I’ve been trying for years to develop computer programs that can understand your intent and use that understanding […]
09 Jan What of Perception

Questions Cognitive Modelers Might Ask The biological and chemical processes associated with brain activity are the foundation on which our exploration of the cognitive mind is built. Yet the physiological underpinnings are not sufficient, in themselves, to lead us to the next cybernetic level. Too many questions are left unanswered. In this section of Understanding […]
08 Jan E/I Electric Potential Curve
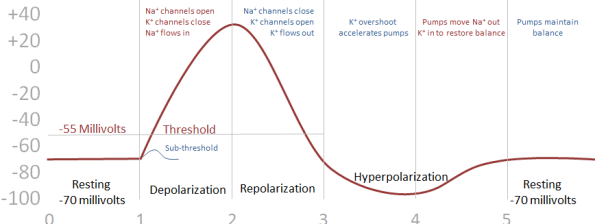
Challenge I’ve noticed two phenomena in computing that have often been compared to brain activity even though they don’t significantly resemble the behavior of electrical potential changes between neurons: Flip-Flop (the changing of a “register” from 0 to 1 Node Firing (The activation of a node in an artificial neural network) In this section of Understanding Context, I’ve been trying to […]
06 Jan Excitation and Inhibition

Most, if not all, neural information-processing functions involve the flow of action potential. Impulses in the nervous system are changes in the action potential or electrical charge of membranes. It is possible that, in addition to the membranes, the potential within the cytoplasm of the cell changes as a result of electrical flow in neurons. […]
03 Jan Synapses and Neurotransmitters

Synapse Structure Electrical impulses are transmitted between neurons either electrically or chemically, with chemical synapses being the most numerous by far. The synapse is where electrical transduction between neurons occurs, facilitating perception, thought and action. The gap between a synapse and its target is called the synaptic cleft (tagged in the center right of the illustration and […]






