abacus
| Keywords | References |
| computer | algorithms logic |
| cybernetics | parallel computing |
| probability | probability |
| system engineering |
Read more...
abstract
 A concept, thought or object not represented by things corporeal. Abstract may also be a representation or reassembly of physical things in a manner that is one or more removes from reality, as in abstract art. Physical things we can perceive through the senses, possibly with the aid of telescopes, microscopes, dyes, etc. Abstract things are ideas that may or may not apply to physical things, but that must be linked somehow in the brain. Since much, or most of what we know is physical, there must be connections between the physical and abstract.
A concept, thought or object not represented by things corporeal. Abstract may also be a representation or reassembly of physical things in a manner that is one or more removes from reality, as in abstract art. Physical things we can perceive through the senses, possibly with the aid of telescopes, microscopes, dyes, etc. Abstract things are ideas that may or may not apply to physical things, but that must be linked somehow in the brain. Since much, or most of what we know is physical, there must be connections between the physical and abstract.
| Keywords | * No References |
| representation | |
| Knowledge Representation | |
| explicit representation | |
| implicit representation | |
| connectionism | |
| associationism |
Read more...
abstraction

| Keywords | References |
| strata polymorphism | context |
| object existential | knowledge representation |
| dimension creativity | logic |
| continuum class | taxonomy |
| composition decomposition | |
| object-oriented inheritance |
Read more...
acetylcholine
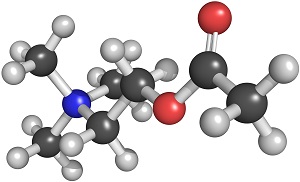 Neurotransmitter chemical CH3--CO--O--CH2--CH2--N--(CH3)3 acetylcholine is liberated from synaptic vesicles to propogate impulses across synapses from axons of motoneurons, and pre- and postganglionic and parasympathetic cholinergic neurons.
Keywords: Amines
channel
neurotransmitter
action potential
E/I
synapse
cholinergic
dopamine
norepinephrine
References: brain physiology
neurons
neuroscience
Hotlinks: Molecular Structure V.2 Cells
Transmission Agents V.3 Nets
Cross Refs: acetylated
Neurotransmitter chemical CH3--CO--O--CH2--CH2--N--(CH3)3 acetylcholine is liberated from synaptic vesicles to propogate impulses across synapses from axons of motoneurons, and pre- and postganglionic and parasympathetic cholinergic neurons.
Keywords: Amines
channel
neurotransmitter
action potential
E/I
synapse
cholinergic
dopamine
norepinephrine
References: brain physiology
neurons
neuroscience
Hotlinks: Molecular Structure V.2 Cells
Transmission Agents V.3 Nets
Cross Refs: acetylated Read more...
ACID
 A transaction standard for database (mostly relational) manipulation that delivers immediate consistency. ACID stands for:
A transaction standard for database (mostly relational) manipulation that delivers immediate consistency. ACID stands for:
- Atomicity: Either the task (or all tasks) within a transaction are performed or none of them are. This is the all-or-none principle. If one element of a transaction fails the entire transaction fails.
- Consistency: The transaction must meet all protocols or rules defined by the system at all times. The transaction does not violate those protocols and the database must remain in a consistent state at the beginning and end of a transaction; there are never any half-completed transactions.
- Isolation: No transaction has access to any other transaction that is in an intermediate or unfinished state. Thus, each transaction is independent unto itself. This is required for both performance and consistency of transactions within a database.
- Durability: Once the transaction is complete, it will persist as complete and cannot be undone; it will survive system failure, power loss and other types of system breakdowns.
Read more...
acquisition
 2. In business finance, buying something out from underneath someone [see 1].
3. In learning, getting knowledge. The types of knowledge we may acquire are patterns governing the use and interpretation of perceptual input including images, sounds, smells, and complex input such as language.
Keywords: epistemology
language
natural language
communication
interpretation
translation
cognition
References: cognition
learning
pattern recognition
2. In business finance, buying something out from underneath someone [see 1].
3. In learning, getting knowledge. The types of knowledge we may acquire are patterns governing the use and interpretation of perceptual input including images, sounds, smells, and complex input such as language.
Keywords: epistemology
language
natural language
communication
interpretation
translation
cognition
References: cognition
learning
pattern recognition Read more...
action
Read more...
action potential
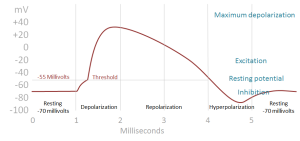 Electromotive potential propagated through electrochemical reactions in brief regenerative pulses along neural or muscle fibers. This electrical flow is divided into positive or excitatory impulses and negative or inhibitory impulses (E/I). The flow of action potential in the brain is chaotic.
Keywords: weight
spike
Schwann cell
resting potential
relay
Ranvier, nodes of
quantal release
pump
permeability
overshoot
oligodendrocyte
norepinephrine
local potential
impulse
exocytosis
endocytosis
efferent
E/I
decay
brain circuitry
anticholinesterase
afferent
acetylcholine
activation
firing
threshold
chaos
neuron
hyperpolarization
depolarization
synapse
neurotransmitter
References: brain physiology
fuzzy logic
neural networks
neurons
neuroscience
Electromotive potential propagated through electrochemical reactions in brief regenerative pulses along neural or muscle fibers. This electrical flow is divided into positive or excitatory impulses and negative or inhibitory impulses (E/I). The flow of action potential in the brain is chaotic.
Keywords: weight
spike
Schwann cell
resting potential
relay
Ranvier, nodes of
quantal release
pump
permeability
overshoot
oligodendrocyte
norepinephrine
local potential
impulse
exocytosis
endocytosis
efferent
E/I
decay
brain circuitry
anticholinesterase
afferent
acetylcholine
activation
firing
threshold
chaos
neuron
hyperpolarization
depolarization
synapse
neurotransmitter
References: brain physiology
fuzzy logic
neural networks
neurons
neuroscience
Read more...
actionable
Read more...
actionable information
 Information that can be acted upon without further analysis. One distinction between "information" and "knowledge" is that information is characterized by associated data elements combined to add meaningfulness, while knowledge is characterized by actionability: the ability to make immediate decisions and take action without seeking additional information or performing complex analyses. As such, the intrinsic value of actionable information is the reduction in time from consumption to realization of value.
Information that can be acted upon without further analysis. One distinction between "information" and "knowledge" is that information is characterized by associated data elements combined to add meaningfulness, while knowledge is characterized by actionability: the ability to make immediate decisions and take action without seeking additional information or performing complex analyses. As such, the intrinsic value of actionable information is the reduction in time from consumption to realization of value. Read more...
activation
 In this blog, activation is used in two contexts:
1) excitatory action potentials as they spread in the brain; and
2) elevated values that are applied to conceptual representations as associations are traversed in an associationist network. In both contexts, activation is capable of heating up entire areas of the network (or cortex) that contain related information.
Keywords: channel
asymptote
action potential
firing
threshold
chaos
neuron
hyperpolarization
depolarization
synapse
neurotransmitter
References: algorithms
brain physiology
fuzzy logic
neural networks
neurons
probability
psychology
In this blog, activation is used in two contexts:
1) excitatory action potentials as they spread in the brain; and
2) elevated values that are applied to conceptual representations as associations are traversed in an associationist network. In both contexts, activation is capable of heating up entire areas of the network (or cortex) that contain related information.
Keywords: channel
asymptote
action potential
firing
threshold
chaos
neuron
hyperpolarization
depolarization
synapse
neurotransmitter
References: algorithms
brain physiology
fuzzy logic
neural networks
neurons
probability
psychology Read more...
adaptation
 Natural systems change through adaptation. Dr. Charles Darwin observed adaptations of Finches. The topography of continents adapts to the flow patterns of wind and water. The link structure of the brain adapts to accommodate new ideas and knowledge. The ability to adapt or learn is needed for systems of the future to be able to perform more brain tasks.
Keywords: learning
exposure
genetics
genetic algorithms
References: algorithms
cybernetics
fuzzy logic
genetics
learning
neural networks
Natural systems change through adaptation. Dr. Charles Darwin observed adaptations of Finches. The topography of continents adapts to the flow patterns of wind and water. The link structure of the brain adapts to accommodate new ideas and knowledge. The ability to adapt or learn is needed for systems of the future to be able to perform more brain tasks.
Keywords: learning
exposure
genetics
genetic algorithms
References: algorithms
cybernetics
fuzzy logic
genetics
learning
neural networks Read more...
adrenergic
 Different kinds of neurons respond to different chemicals. Synapses (or neurons) that respond to the neurotransmitter adrenaline (epinephrine) are adrenergic.
Keywords: norepinephrine
neurotransmitter
cholinergic
neuron
References: brain physiology
neural networks
neurons
Different kinds of neurons respond to different chemicals. Synapses (or neurons) that respond to the neurotransmitter adrenaline (epinephrine) are adrenergic.
Keywords: norepinephrine
neurotransmitter
cholinergic
neuron
References: brain physiology
neural networks
neurons Read more...
afferent
 Axon fibers that conduct impulses toward the brain, or within the brain toward the center of the neuron. In the computational metaphor, an afferent would be represented by an input device or channel such as a keyboard, mouse or microphone. Afferent neurons are peripheral sensory neurons that collect information from the body and transmit it toward the central nervous system.
Keywords: action potential
axon
E/I
nerve fiber
input
output
efferent
References: brain physiology
neurons
neuroscience
Axon fibers that conduct impulses toward the brain, or within the brain toward the center of the neuron. In the computational metaphor, an afferent would be represented by an input device or channel such as a keyboard, mouse or microphone. Afferent neurons are peripheral sensory neurons that collect information from the body and transmit it toward the central nervous system.
Keywords: action potential
axon
E/I
nerve fiber
input
output
efferent
References: brain physiology
neurons
neuroscience Read more...
agent
Read more...
AI
Read more...
algorithm
 A process flow description. Computers run on algorithms or sets of instructions that describe the process flow in detail. The robustness of an algorithm is a measure of how well it accomplishes the purpose for which it is intended.
Keywords: state space
image processing
ATN
robust
schemata
problem
design
branching
computer
process
heuristic
causal relations
References: AI programming
algorithms
automata
computing
formalisms
logic
rules
A process flow description. Computers run on algorithms or sets of instructions that describe the process flow in detail. The robustness of an algorithm is a measure of how well it accomplishes the purpose for which it is intended.
Keywords: state space
image processing
ATN
robust
schemata
problem
design
branching
computer
process
heuristic
causal relations
References: AI programming
algorithms
automata
computing
formalisms
logic
rules Read more...
ALife (Artificial Life)
Read more...
ambiguity
Read more...
amines
Read more...
amnesia
Read more...
amygdala
Read more...
analog
Read more...
analysis
 1) The process of breaking apart or disassembling a thing, often abstract or intangible, for the intent of understanding it. In computing professions, analysis precedes (or should precede) design. The opposite of analysis is synthesis. Cybernetics is, by definition, synthetic.
2) The first phase in an automation project in which the business and technical requirements are gathered and formalized into a business systems analysis to serve as the basis for system design.
Keywords: pragmatics
parsing
meaningful
design
descriptive relations
synthesis
statistical analysis
probability
stochastic
process
References: algorithms
computing
context
fuzzy logic
inference
perception
1) The process of breaking apart or disassembling a thing, often abstract or intangible, for the intent of understanding it. In computing professions, analysis precedes (or should precede) design. The opposite of analysis is synthesis. Cybernetics is, by definition, synthetic.
2) The first phase in an automation project in which the business and technical requirements are gathered and formalized into a business systems analysis to serve as the basis for system design.
Keywords: pragmatics
parsing
meaningful
design
descriptive relations
synthesis
statistical analysis
probability
stochastic
process
References: algorithms
computing
context
fuzzy logic
inference
perception Read more...
anaphora
Read more...
android
Read more...
ANS
Read more...
anticholinesterase
Read more...
anxiety
Read more...
aphasia
Read more...
API
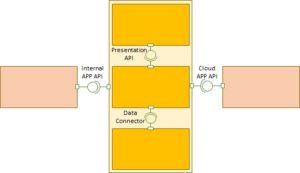 Application Programmer Interface. I define API as a predefined protocol for connecting two coded objects together for the purpose of information or process exchange. The coded objects may be of the same type, or different, and may be applications or applets, services or microservices, operating systems or solutions or embedded code that controls hardware. This is a very ambiguous term, and yet, as is common with many terms, the definitions cluster closely together.
Here is a definition that focuses on programmers working inside solutions: WeboPedia
Here's one that emphasizes control systems such as operating systems: PCMag
Here's another that dwells on applications or solutions interacting: ReadWrite
Kevin Stanton provides a definition of APIs that I think is most applicable in 2016. His definition is published at Sprout Social.
“API is a precise specification written by providers of a service that programmers must follow when using that service... It describes what functionality is available, how it must be used and what formats it will accept as input or return as output. In recent years, the term API colloquially is used to describe both the specification and service itself, e.g., the Facebook Graph API.”
Application Programmer Interface. I define API as a predefined protocol for connecting two coded objects together for the purpose of information or process exchange. The coded objects may be of the same type, or different, and may be applications or applets, services or microservices, operating systems or solutions or embedded code that controls hardware. This is a very ambiguous term, and yet, as is common with many terms, the definitions cluster closely together.
Here is a definition that focuses on programmers working inside solutions: WeboPedia
Here's one that emphasizes control systems such as operating systems: PCMag
Here's another that dwells on applications or solutions interacting: ReadWrite
Kevin Stanton provides a definition of APIs that I think is most applicable in 2016. His definition is published at Sprout Social.
“API is a precise specification written by providers of a service that programmers must follow when using that service... It describes what functionality is available, how it must be used and what formats it will accept as input or return as output. In recent years, the term API colloquially is used to describe both the specification and service itself, e.g., the Facebook Graph API.”
Read more...
arborization
 Branching of nerve fibers or the actual dendrites or axons that are the branches. Arborization is one characteristic of neurons that uniquely enables them to perform cybernetic functions.
Keywords: branching
dendrite
nerve fiber
axon
neurite
References: brain physiology
neurons
neuroscience
Branching of nerve fibers or the actual dendrites or axons that are the branches. Arborization is one characteristic of neurons that uniquely enables them to perform cybernetic functions.
Keywords: branching
dendrite
nerve fiber
axon
neurite
References: brain physiology
neurons
neuroscience Read more...
architecture
Read more...
argument
Read more...
arity
 Arity is used in relational databases and logical propositions to describe the number of arguments a function or relation is expected to possess. Relational database arities are one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-many and variations that include the possibility of none. Functional arities are the number of arguments or relations needed to form a complete proposition or function.
See: http://logic.stanford.edu/dataintegration/chapters/chap02.html
Keywords: relation
function
form
argument
References: algorithms
automata
computing
formalisms
logic
rules
syntax
Arity is used in relational databases and logical propositions to describe the number of arguments a function or relation is expected to possess. Relational database arities are one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-many and variations that include the possibility of none. Functional arities are the number of arguments or relations needed to form a complete proposition or function.
See: http://logic.stanford.edu/dataintegration/chapters/chap02.html
Keywords: relation
function
form
argument
References: algorithms
automata
computing
formalisms
logic
rules
syntax Read more...
arousal
Read more...
ART
Read more...
association
Read more...
astrocyte
Read more...
asymptote
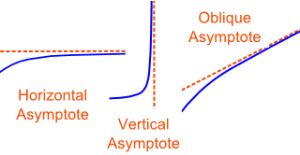 An asymptotic function, common to neural networks, is a curve that approaches an intersection with a straight line on the same plane, but they never meet.
An asymptotic curve (Math is Fun)
An asymptotic function, common to neural networks, is a curve that approaches an intersection with a straight line on the same plane, but they never meet.
An asymptotic curve (Math is Fun)
| Keywords | References |
| threshold | AI programming |
| activation | algorithms automata |
| spike | computing formalisms |
| E/I | logic Rules |
Read more...
ATN
Read more...
ATP
Read more...
attention
Read more...
automata
Read more...
automated data processing
Read more...
autonomic nervous system
Read more...
autonomous computing agents
Read more...
autonomous land vehicle (ALV)
 Posts with reference to autonomous land vehicle technology: Pattern Recognition in Two Dimensions Understanding what we See
A bit from Gizmodo on the history of ALVs in America
Posts with reference to autonomous land vehicle technology: Pattern Recognition in Two Dimensions Understanding what we See
A bit from Gizmodo on the history of ALVs in America Read more...
axon
Read more...
axoplasm
Read more...
backpropagation
The Backpropagation Algorithm
- 1.
- Propagates inputs forward in the usual way, i.e.
- All outputs are computed using sigmoid thresholding of the inner product of the corresponding weight and input vectors.
- All outputs at stage n are connected to all the inputs at stage n+1
- 2.
- Propagates the errors backwards by apportioning them to each unit according to the amount of this error the unit is responsible for.
 input vector for unit j (xji = ith input to the jth unit)
input vector for unit j (xji = ith input to the jth unit) weight vector for unit j (wji = weight on xji)
weight vector for unit j (wji = weight on xji) , the weighted sum of inputs for unit j
, the weighted sum of inputs for unit j- oj = output of unit j (
 )
) - tj = target for unit j
- Downstream(j) = set of units whose immediate inputs include the output of j
- Outputs = set of output units in the final layer



- 1. For each unit k downstream from j, zk is a function of zj
- 2. The contribution to error by all units
 in the same layer as j is independent of wji
in the same layer as j is independent of wji

 . Substituting,
. Substituting,

- Create a feed-forward network with ni inputs, nh hidden units, and no output units.
- Initialize all the weights to small random values (e.g., between -.05 and .05)
- Until termination condition is met, Do
- For each training example
 , Do
, Do- 1. Input the instance
 and compute the output ou of every unit.
and compute the output ou of every unit. - 2. For each output unit k, calculate
-

- 3. For each hidden unit h, calculate
-

- 4. Update each network weight wji as follows:
-

- 1. Input the instance
- For each training example
Read more...
BASE
 Most relational databases support ACID transactions, that rely on a single data store (often on a single disk or cluster of a handful of disks. Big Data often runs on dozens, hundreds or thousands of physical disk drives, and use BASE transactions to spread out the data and improve resilience. The improvements come when there are a high volume of concurrent transactions, and when one or more physical drives fail.
A transaction standard for database (mostly big data) manipulation that delivers eventual consistency. BASE stands for:
Most relational databases support ACID transactions, that rely on a single data store (often on a single disk or cluster of a handful of disks. Big Data often runs on dozens, hundreds or thousands of physical disk drives, and use BASE transactions to spread out the data and improve resilience. The improvements come when there are a high volume of concurrent transactions, and when one or more physical drives fail.
A transaction standard for database (mostly big data) manipulation that delivers eventual consistency. BASE stands for:
- Basically Available: This constraint states that the system does guarantee the availability of the data as regards CAP Theorem; there will be a response to any request. But, that response could still be ‘failure’ to obtain the requested data or the data may be in an inconsistent or changing state, much like waiting for a check to clear in your bank account.
- Soft state: The state of the system could change over time, so even during times without input there may be changes going on due to ‘eventual consistency,’ thus the state of the system is always ‘soft.’
- Eventual consistency: The system will eventually become consistent once it stops receiving input. The data will propagate to everywhere it should sooner or later, but the system will continue to receive input and is not checking the consistency of every transaction before it moves onto the next one. Werner Vogel’s article “Eventually Consistent - Revisited” covers this topic is much greater detail.
Read more...
basket cells
Read more...
Bayes' Theorem
 Bayes' Theorem is a mathematical equation for calculating evidence-based probability. Reverend Thomas Bayes, University of Edinburgh (1701-1761) described how the probability (P) of a specific theoretical (T) outcome is affected by a new piece of evidence (E). The beauty of this theory and its use in conceptual networks is that it does not limit the number of constraints you can apply to solving a problem or obtaining an outcome. (There's no surviving likeness of the man)
Bayes' Theorem is a mathematical equation for calculating evidence-based probability. Reverend Thomas Bayes, University of Edinburgh (1701-1761) described how the probability (P) of a specific theoretical (T) outcome is affected by a new piece of evidence (E). The beauty of this theory and its use in conceptual networks is that it does not limit the number of constraints you can apply to solving a problem or obtaining an outcome. (There's no surviving likeness of the man)
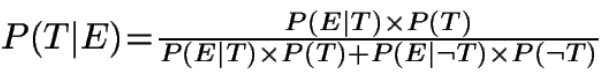 Trinity
Mathematical Formulas from Wolfram
Better Explained
Bayesian Network
probability
inference
constraint
Trinity
Mathematical Formulas from Wolfram
Better Explained
Bayesian Network
probability
inference
constraint Read more...
Bayesian Network
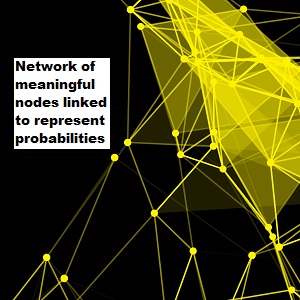 A Bayesian Network is a formalized linked collection of named nodes with propositional links used in classical multivariate probabalistic systems to predict outcomes. These networks are used and studied in fields such as statistics, systems engineering, information theory, pattern recognition and statistical mechanics.
Murphy, K. at UBC
Bayesian Theorem
probability
chaos
inference
A Bayesian Network is a formalized linked collection of named nodes with propositional links used in classical multivariate probabalistic systems to predict outcomes. These networks are used and studied in fields such as statistics, systems engineering, information theory, pattern recognition and statistical mechanics.
Murphy, K. at UBC
Bayesian Theorem
probability
chaos
inference Read more...
behavior
Read more...
belief
Read more...
Big Data
Read more...
binding
Read more...
blackboard
Read more...
boundaries
Read more...
BPM
 Business Process Modeling: Application development methods based on process flow-diagramming that can effectively be automated using high Speed, low code tools and standards including BPMN 2.0 (BPM Notation) and BPEL (Business Process Execution Language).
Gartner says: "Business process management (BPM) is a discipline that uses various methods to discover, model, analyze, measure, improve, and optimize business processes. A business process coordinates the behavior of people, systems, information, and things to produce business outcomes in support of a business strategy. Processes can be structured and repeatable or unstructured and variable. Though not required, technologies are often used with BPM. BPM is key to align IT/OT investments to business strategy (http://www.gartner.com/it-glossary/business-process-management-bpm/).
Business Process Modeling: Application development methods based on process flow-diagramming that can effectively be automated using high Speed, low code tools and standards including BPMN 2.0 (BPM Notation) and BPEL (Business Process Execution Language).
Gartner says: "Business process management (BPM) is a discipline that uses various methods to discover, model, analyze, measure, improve, and optimize business processes. A business process coordinates the behavior of people, systems, information, and things to produce business outcomes in support of a business strategy. Processes can be structured and repeatable or unstructured and variable. Though not required, technologies are often used with BPM. BPM is key to align IT/OT investments to business strategy (http://www.gartner.com/it-glossary/business-process-management-bpm/). Read more...
brain
Read more...
brain circuitry
Read more...
brain development
Read more...
brain stem
Read more...
branching
Read more...
Broca's area
Read more...
Brodmann
Read more...
business intelligence
 Multi-dimensional analytics in business modeling and reporting has an assumed name: business intelligence (BI). A relational database is basically two dimensional with tables and columns in one dimension and primary and foreign keys in another. Multi-dimensional analytics involve "cubes" and "star schemas" that create formal edges binding together different dimensions. Each dimension is defined as a semantic concept with a set of attributes and facts. This muti-dimensionality empowers business analysts with better insights as it permits deeper analytics, advanced filtering and sorting and a variety of views that answer more complex questions than typical reports.
Webopedia on BI
data
Big Data
Multi-dimensional analytics in business modeling and reporting has an assumed name: business intelligence (BI). A relational database is basically two dimensional with tables and columns in one dimension and primary and foreign keys in another. Multi-dimensional analytics involve "cubes" and "star schemas" that create formal edges binding together different dimensions. Each dimension is defined as a semantic concept with a set of attributes and facts. This muti-dimensionality empowers business analysts with better insights as it permits deeper analytics, advanced filtering and sorting and a variety of views that answer more complex questions than typical reports.
Webopedia on BI
data
Big Data
Read more...
C/S
Read more...
canonical model
 Canonical models are logical level semantic graphs, and can be used for both data and processes. "Canonical" implies a top-level prescribed set of rules that define orderliness and, when adhered to, oppose chaos. A canonical data model (CDM) defines the core content entities associated with a specific domain, their semantic meanings, attributes, and associations with other elements. A canonical process model describes top-level processes and sequences needed to comply and to accomplish a mission. Both canonical data and process models serve as reference models, forming abstract, general frameworks to support specific implementations.
Canonical models are logical level semantic graphs, and can be used for both data and processes. "Canonical" implies a top-level prescribed set of rules that define orderliness and, when adhered to, oppose chaos. A canonical data model (CDM) defines the core content entities associated with a specific domain, their semantic meanings, attributes, and associations with other elements. A canonical process model describes top-level processes and sequences needed to comply and to accomplish a mission. Both canonical data and process models serve as reference models, forming abstract, general frameworks to support specific implementations.
Read more...
categorize
Read more...
causal relation
 One method of defining knowledge is to represent cause and effect as related entities. A causal relation links causes to effects in an understandable way, such as is done in a logical theorem (e.g. if it rains, then plants will grow). The relation between a cause and its effect or between regularly correlated events or phenomena may be intentional (or the result of some organisms intended action) or natural (some event in the physical universe that follows the normal course of the interaction of particles and objects). See Causal Chains in Action.
Keywords: relation
modus tollens
modus ponens
interaction
experience
existential
common sense
algorithm
hierarchical relations
knowledge
logical form
References:
Merriam Webster Stanford
algorithms
associationism
learning
logic
rules
taxonomy
One method of defining knowledge is to represent cause and effect as related entities. A causal relation links causes to effects in an understandable way, such as is done in a logical theorem (e.g. if it rains, then plants will grow). The relation between a cause and its effect or between regularly correlated events or phenomena may be intentional (or the result of some organisms intended action) or natural (some event in the physical universe that follows the normal course of the interaction of particles and objects). See Causal Chains in Action.
Keywords: relation
modus tollens
modus ponens
interaction
experience
existential
common sense
algorithm
hierarchical relations
knowledge
logical form
References:
Merriam Webster Stanford
algorithms
associationism
learning
logic
rules
taxonomy
Read more...
cell
Read more...
central nervous system
Read more...
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
 Computers, and other digital devices like phones and tablets, are built around central processing units (CPUs) and other components that involve computer chips or chipsets. These guys perform most of the computational heavy lifting, so they are like the brains of computers.
Computers, and other digital devices like phones and tablets, are built around central processing units (CPUs) and other components that involve computer chips or chipsets. These guys perform most of the computational heavy lifting, so they are like the brains of computers. Read more...
cerebellum
Read more...
cerebrum
Read more...
certainty
Read more...
channel
Read more...
chaos
Read more...
cholinergic
Read more...
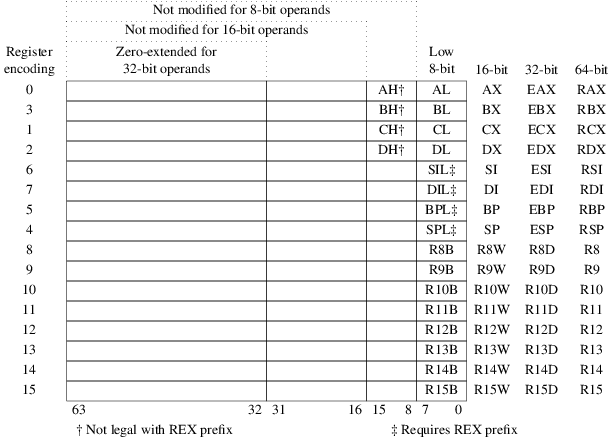
CISC
Read more...
citizen developer
Read more...
class
Read more...
classification
Read more...
climbing fibers
Read more...
Code
Read more...
cognition
Read more...
cognitive computing
Read more...
cognitive modeling
Read more...
Cognitive Science
Read more...
combinatorial explosion
Read more...
combinatorial explosion
Read more...
common sense
Read more...
communication
Read more...
composition
Read more...
comprehension
Read more...
computational linguistics

Read more...
computer
 A mechanical device used to automatically process data (not your brain - it's different)
A mechanical device used to automatically process data (not your brain - it's different)- A Programmable Calculator
- A mobile phone or Pad device (iPad/Android)
- The thing that keeps your car, refrigerator, wristwatch and heart rhythm running
| Keywords | References |
| tools | AI programming |
| GUI | algorithms |
| architecture | automata |
| software | computing |
| RAM | formalisms |
| program | logic |
| design | rules |
| C/S | |
| algorithm | |
| abacus | |
| cybernetics | |
| modeling | |
| brain | |
Read more...
computing
Read more...
concept
Read more...
concept learning
 Concept learning, category learning or concept acquisition/attainment is a distinct type of learning, human or machine, characterized by construction of an associative meaning model. From a psychology wiki, "concepts are the mental categories that help us classify objects, events, or ideas and each object, event, or idea has a set of common relevant features. Thus, concept learning is a strategy which requires a learner to compare and contrast groups or categories that contain concept-relevant features with groups or categories that do not contain concept-relevant features." The set of common relevant features represent associations with taxonomical generalization. Concept learning can go beyond taxonomies to causality, meronomy, identity, time and space, and narrower domains such as geopolitics manufacturing processes.
Concept learning, category learning or concept acquisition/attainment is a distinct type of learning, human or machine, characterized by construction of an associative meaning model. From a psychology wiki, "concepts are the mental categories that help us classify objects, events, or ideas and each object, event, or idea has a set of common relevant features. Thus, concept learning is a strategy which requires a learner to compare and contrast groups or categories that contain concept-relevant features with groups or categories that do not contain concept-relevant features." The set of common relevant features represent associations with taxonomical generalization. Concept learning can go beyond taxonomies to causality, meronomy, identity, time and space, and narrower domains such as geopolitics manufacturing processes. Read more...
conceptual
Read more...
conceptual graph
Read more...
conclusion
Read more...
confidence
Read more...
connectionism
Read more...
Connectomics
Read more...
consciousness
Read more...
constraint
 A factor that affects or limits a decision or outcome. In decision making (particularly automated), it is important to limit the problem space to a manageable number of questions whose answers influence the final outcome. However, missing important constraints in evaluating a problem can lead to skewed or incorrect or unsuitable outcomes. Constraint-based reasoning attempts to prioritize the answers to all the pertinent questions and, based on the weighted sum, arrive at a decision.
Keywords: feature
sample space
range
inference
logic
fuzzy logic
stochastic
References: algorithms
automata
computing
formalisms
logic
rules
syntax
Posts:
Generating and Qualifying Propositions
Framing Formal Logic
A factor that affects or limits a decision or outcome. In decision making (particularly automated), it is important to limit the problem space to a manageable number of questions whose answers influence the final outcome. However, missing important constraints in evaluating a problem can lead to skewed or incorrect or unsuitable outcomes. Constraint-based reasoning attempts to prioritize the answers to all the pertinent questions and, based on the weighted sum, arrive at a decision.
Keywords: feature
sample space
range
inference
logic
fuzzy logic
stochastic
References: algorithms
automata
computing
formalisms
logic
rules
syntax
Posts:
Generating and Qualifying Propositions
Framing Formal Logic Read more...
context
 The situation/environment in which cognitive (and all other) activities occur. Place, time, and all sensory inputs (i.e. anything we can perceive in our surroundings) constitute the components of context. We filter out unnecessary details and focus on meaningful details such as who and what major objects are present.
The situation/environment in which cognitive (and all other) activities occur. Place, time, and all sensory inputs (i.e. anything we can perceive in our surroundings) constitute the components of context. We filter out unnecessary details and focus on meaningful details such as who and what major objects are present.
- from Latin contextus: an assembling or putting together,
- from contexere: to interweave more than one thing,
- from com-: together + texere: to weave or braid
Read more...
context-free
Read more...
context-sensitive
Read more...
continuum
Read more...
convergence
 We are experiencing two great movements toward convergence in previously separate technologies:
We are experiencing two great movements toward convergence in previously separate technologies:
- Voice and Data Convergence in which IP telephony is enabling telephone and wireless phone communications to share the same wires and bandwidth as data communications
- Structured and Unstructured Content Convergence in which databases (structured data) automatically mingle with documents, videos, images and sound files to bring users richer experiences.
Read more...
correlation
Read more...
cortex
Read more...
corticospinal tract
Read more...
creativity
Read more...
cue
Read more...
cybernetics
Read more...
cyberspace
Read more...
cytoarchitecture
Read more...
cytoplasm
Read more...
cytoskeleton
Read more...
data
Read more...
data processing
Read more...
data type
Read more...
data-driven
Read more...
database
 When digital information is structured in a table or tables or rows and columns, especially named columns where the name of each column describes what content appears in that column for each row. Rows are described as records, and each record is usually assigned a unique ID. Data in different tables are associated with each other based on data in one or more of the columns, often using primary and foreign keys and accessed by a common language such as Structured Query Language or SQL (SQL Keys). An RDBMS is a relational database management system provides storage management and functionality needed to efficiently index, access and transact data (CRUD is Create, Read, Update and Delete).
see structured content
When digital information is structured in a table or tables or rows and columns, especially named columns where the name of each column describes what content appears in that column for each row. Rows are described as records, and each record is usually assigned a unique ID. Data in different tables are associated with each other based on data in one or more of the columns, often using primary and foreign keys and accessed by a common language such as Structured Query Language or SQL (SQL Keys). An RDBMS is a relational database management system provides storage management and functionality needed to efficiently index, access and transact data (CRUD is Create, Read, Update and Delete).
see structured content Read more...
dead man's hand
Read more...
decay
Read more...
decision
Read more...
decision support system
Read more...
declarative knowledge
Read more...
declarative memory
Read more...
decomposition
Read more...
deductive reasoning
 Deductive reasoning takes existential and/or universal statements about knowledge, or generalizations, then uses a process similar to classification to infer specific instances or phenomena that match the pattern of the generalization. Scientific methods use deduction to test a theory beginning with a general statement, or hypothesis, and examining the possible outcomes or similarities to reach a specific, logical conclusion.
Livescience on Deductive vs. Inductive reasoning
Deductive reasoning takes existential and/or universal statements about knowledge, or generalizations, then uses a process similar to classification to infer specific instances or phenomena that match the pattern of the generalization. Scientific methods use deduction to test a theory beginning with a general statement, or hypothesis, and examining the possible outcomes or similarities to reach a specific, logical conclusion.
Livescience on Deductive vs. Inductive reasoning Read more...
Deep Language Understanding
Read more...
deixis
Read more...
dementia
Read more...
dendrite
Read more...
depolarization
Read more...
descriptive relation
Read more...
design
Read more...
determinism
Read more...
DevOps
Read more...
dichotomous logic
Read more...
diencephalon
Read more...
differentiation
Read more...
digital
Read more...
digital consumability
 Consumability is predictably ambiguous. IBM uses the term to mean "assets available on machines in a LoadLeveler® cluster." but consumability means "a client's complete experience with a technology solution beginning with buying the right product to updating it." This is not what I'm talking about. Digital consumability, in the context of this blog, is a property of digital information involving formats accessible to multiple systems and processes (such as heuristics) that may benefit from it. This means that systems that didn't create it and don't manage it can get it and use it to bring some value. Many Legacy computing systems are unable to adapt their behavior based on consuming external data. But as more "services", micro-services, and cognitive computing systems arise in an IT ecosystem where API's facilitate interconnections between systems, the importance of rich consumable digital information increases, and creates opportunities to add intelligence to existing processes.
Consumability is predictably ambiguous. IBM uses the term to mean "assets available on machines in a LoadLeveler® cluster." but consumability means "a client's complete experience with a technology solution beginning with buying the right product to updating it." This is not what I'm talking about. Digital consumability, in the context of this blog, is a property of digital information involving formats accessible to multiple systems and processes (such as heuristics) that may benefit from it. This means that systems that didn't create it and don't manage it can get it and use it to bring some value. Many Legacy computing systems are unable to adapt their behavior based on consuming external data. But as more "services", micro-services, and cognitive computing systems arise in an IT ecosystem where API's facilitate interconnections between systems, the importance of rich consumable digital information increases, and creates opportunities to add intelligence to existing processes. Read more...
dimension
Read more...
disambiguation
Read more...
discern
Read more...
discriminate
Read more...
distributed
Read more...
DNA
Read more...
domain
Read more...
dopamine
Read more...
dualism
Read more...
E/I
Read more...
eclecticism
Read more...
efferent
Read more...
Electrical Current
Read more...
eliminativism
Read more...
emotion
Read more...
empiricism
Read more...
endocytosis
Read more...
English
Read more...
Enterprise Knowledge Management (EKM)
 Depending on the maturity of the organization, EKM can mean anything from organizing educational content (packaged learning materials), to enabling the semantic enterprise with machine learning, natural language search and query, converged metadata management and knowledge curation and governance processes and tools. In the basic case, a catalog and managing sources of record and publishing processes are enough to bring significant business value. In advanced cases, at the end of major investment, organizations develop competitive advantage with rapid insights into changes in consumer behaviors and market pressures.
Depending on the maturity of the organization, EKM can mean anything from organizing educational content (packaged learning materials), to enabling the semantic enterprise with machine learning, natural language search and query, converged metadata management and knowledge curation and governance processes and tools. In the basic case, a catalog and managing sources of record and publishing processes are enough to bring significant business value. In advanced cases, at the end of major investment, organizations develop competitive advantage with rapid insights into changes in consumer behaviors and market pressures. Read more...
entropy
Read more...
environment
 An ecosystem of capabilities a software engineer uses to weave magic digital fabric.
TutorialsPoint says: Though Environment Setup is not an element of any Programming Language, it is the first thing we need to start programming with any Programming Language. you will need following setup to start with programming using any programming language.
An ecosystem of capabilities a software engineer uses to weave magic digital fabric.
TutorialsPoint says: Though Environment Setup is not an element of any Programming Language, it is the first thing we need to start programming with any Programming Language. you will need following setup to start with programming using any programming language.
- A text editor to create computer program.
- A compiler to compile program into binary format.
- An interpreter to execute program directly.
Read more...
episodic knowledge
Read more...
epistemology
Read more...
equation
Read more...
ERP - Event Related Potential
- Evoked Response Potential: Electric flow in the brain resulting from some external stimuli
- Event Related Potential: Electric flow in the brain resulting from some external stimuli
- Enterprise Resource Planning: An amalgam of processes often associated with financial accounting, supply, demand, manufacturing, selling and/or fulfilling in commerce.
- Visual evoked response or potential (VER or VEP), which is when the eyes are stimulated by looking at a test pattern.
- Auditory brain stem evoked response or potential (ABER or ABEP), which is when hearing is stimulated by listening to a test tone.
- Somatosensory evoked response or potential (SSER or SSEP), which is when the nerves of the arms and legs are stimulated by an electrical pulse.
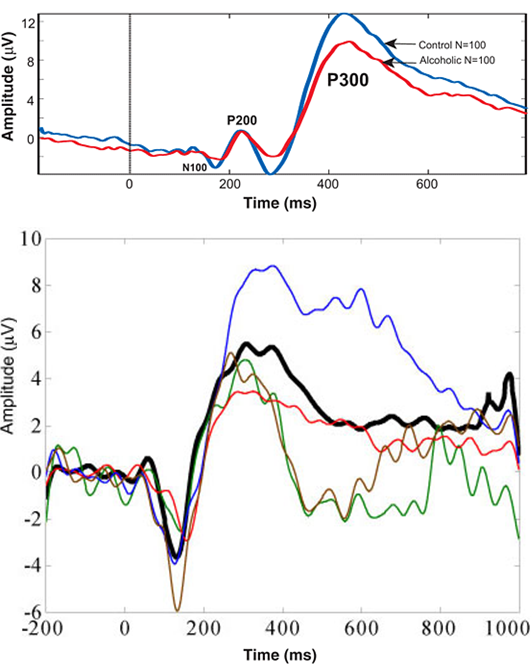
| Keywords | References |
| action potential | The Curve |
| impulse | |
| E/I |
Read more...
Every nation, kindred, tongue and people
Read more...
exception
Read more...
existential
Read more...
exocytosis
Read more...
expectations
Read more...
experience
Read more...
experiment
Read more...
expert system
Read more...
explanation utility
 In AI, explanation utilities provide details about a model's output such as the lineage of the data used, salient features in the model or the specific inference rules fired to derive the results. With processes that are too complex or untraceable to support detailed explanation, such as neural network-based classification, the size or nature of the training set may be the closest corrollary. Knowing how much each feature or element in the model contributed to the result can help find gaps in training or errors in the model, or manually train weights of contributing elements. Explanations can also be used to recognize bias in the model and verify that the model is behaving as expected.
In AI, explanation utilities provide details about a model's output such as the lineage of the data used, salient features in the model or the specific inference rules fired to derive the results. With processes that are too complex or untraceable to support detailed explanation, such as neural network-based classification, the size or nature of the training set may be the closest corrollary. Knowing how much each feature or element in the model contributed to the result can help find gaps in training or errors in the model, or manually train weights of contributing elements. Explanations can also be used to recognize bias in the model and verify that the model is behaving as expected. Read more...
explicit representation
Read more...
exposure
Read more...
expression
Read more...
expressiveness
Read more...
extra-sensory
Read more...
fact
Read more...
feature
Read more...
feedback
Read more...
filtering
Read more...
firing
Read more...
flip-flop
flip-flop
 1) A politician changing his position
2) A single register in memory or a processor of a circuit, particularly an integrated circuit, is called a flip-flop. Transistors and gates are used to store a charge that represents 1 or 0 in digital logic.
3) Either a left or a right beach style sandal (ie. the singular of flip-flops)
1) A politician changing his position
2) A single register in memory or a processor of a circuit, particularly an integrated circuit, is called a flip-flop. Transistors and gates are used to store a charge that represents 1 or 0 in digital logic.
3) Either a left or a right beach style sandal (ie. the singular of flip-flops)
| Keywords | References |
| memory Short-Term Memory | algorithms |
| data data processing ADP | automata |
| digital | computing |
| dichotomous logic | logic |
Read more...
forget
Read more...
form
Read more...
formalism
Read more...
fractal
Read more...
frame
Read more...
frenetic
Read more...
function
Read more...
fusiform cells
fusiform cells
A type of neuron found in the cerebrum, characterized by different shapes (sorry for the vague definition – why don't you read about it in one of the pages here?). Modeling Neural Interconnections Varieties of Nerve Cells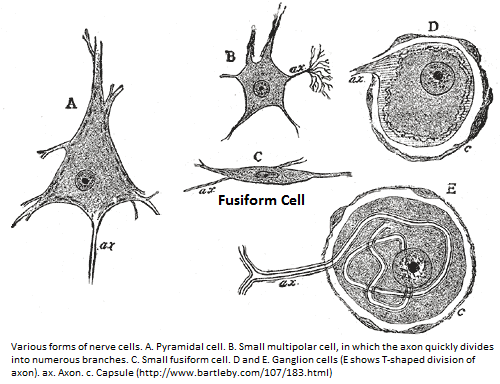
| Keywords | References |
| cerebrum | brain physiology |
| stellate cells | neurons |
| basket cells | neuroscience |
| neurogliaform | |
Read more...
fuzzy
Read more...
fuzzy logic
 A form of reasoning that incorporates multiple criteria for making decisions and multiple values for evaluating possibilities. Fuzzy logic differs from dichotomous logic in that, while dichotomous logic expects to derive a solution by deciding whether each of the constraints or parameters is true or false, fuzzy reasoning permits scales of conditions and shades of values. It is less interested in truth and more in practicality.
Fuzzy Logic and the Mind-Brain Dichotomy
Context Powers Backward Chaining Logic
Dichotomy vs. Continuum
A form of reasoning that incorporates multiple criteria for making decisions and multiple values for evaluating possibilities. Fuzzy logic differs from dichotomous logic in that, while dichotomous logic expects to derive a solution by deciding whether each of the constraints or parameters is true or false, fuzzy reasoning permits scales of conditions and shades of values. It is less interested in truth and more in practicality.
Fuzzy Logic and the Mind-Brain Dichotomy
Context Powers Backward Chaining Logic
Dichotomy vs. Continuum
| Keywords | References |
| paradox | algorithms |
| exception | associationism |
| chaos | chaos |
| constraint | connectionism |
| confidence | fuzzy logic |
| logic belief | neural networks |
| multi-valued logic | learning |
| determinism non-determinism | |
| dichotomous logic | |
| fuzzy AI | pattern recognition |
Read more...
gamification
Read more...
Gamma Oscillations
Read more...
generalization
Read more...
Generative Pretrained Transformers (GPT)
Read more...
genetic algorithms
Read more...
genetics
Read more...
GIGO
Read more...
gnostic
Read more...
Golgi cells
Read more...
governance
Read more...
graceful degradation
Read more...
grammar
Read more...
granularity
Read more...
granule cells
Read more...
gray matter
Read more...
GUI
Read more...
gyrus
Read more...
Hadoop
 Hadoop refers to an open source big data system and software library is a framework that supports distributed processing for large data sets using clusters of computers and simple programming models. It can be deployed on a single server, or up to thousands of machines, distributing both computation and storage capabilities needed to handle the increasing volume, velocity and variety of information in today's interconnected world.
http://hadoop.apache.org/
Hadoop refers to an open source big data system and software library is a framework that supports distributed processing for large data sets using clusters of computers and simple programming models. It can be deployed on a single server, or up to thousands of machines, distributing both computation and storage capabilities needed to handle the increasing volume, velocity and variety of information in today's interconnected world.
http://hadoop.apache.org/ Read more...
heredity
Read more...
heuristic
Read more...
hierarchical relation
Read more...
hippocampus
Read more...
horizontal cells
Read more...
hybrid IT
Read more...
hypermnesia
Read more...
hyperpolarization
Read more...
hypertext
Read more...
hypothalamus
Read more...
iatric
Read more...
idiom
Read more...
image processing
Read more...
imagination
Read more...
impedance mismatch
 Object-oriented programming languages enable developers to build systems, services and applications out of objects that have both data and behavior (methods). Relational databases store data in tables bound together through primary and foreign keys. Object-oriented programming is based on time-tested software engineering principles while the "relational" paradigm is based on mathematical principles. Because the underlying paradigms are different the two technologies require an intervening transformation layer to work together seamlessly. "The impedance mismatch becomes apparent when you look at the preferred approach to access: With the object paradigm you traverse objects via their relationships whereas with the relational paradigm you join the data rows of tables. This fundamental difference results in a non-ideal combination of object and relational technologies" (Scott Wambler at Agile Data).
Object-oriented programming languages enable developers to build systems, services and applications out of objects that have both data and behavior (methods). Relational databases store data in tables bound together through primary and foreign keys. Object-oriented programming is based on time-tested software engineering principles while the "relational" paradigm is based on mathematical principles. Because the underlying paradigms are different the two technologies require an intervening transformation layer to work together seamlessly. "The impedance mismatch becomes apparent when you look at the preferred approach to access: With the object paradigm you traverse objects via their relationships whereas with the relational paradigm you join the data rows of tables. This fundamental difference results in a non-ideal combination of object and relational technologies" (Scott Wambler at Agile Data). Read more...
implicit representation
Read more...
impossible
Read more...
impulse
Read more...
inductive reasoning
 Inductive reasoning is a bottom-up or forward-chaining model that makes broad generalizations about knowledge based on specific facts or observations. In a step-by-step process or computer program, inductive reasoning techniques may look at the facts or variable values you have accumulated so far, then branch based on a rule that applies to those variables.
Livescience on Deductive vs. Inductive reasoning
Inductive reasoning is a bottom-up or forward-chaining model that makes broad generalizations about knowledge based on specific facts or observations. In a step-by-step process or computer program, inductive reasoning techniques may look at the facts or variable values you have accumulated so far, then branch based on a rule that applies to those variables.
Livescience on Deductive vs. Inductive reasoning Read more...
inference
Read more...
information
Read more...
inheritance
Read more...
innate
Read more...
input
Read more...
instinctive
Read more...
integration
Read more...
intelligence
Read more...
interaction
Read more...
intermediate filaments
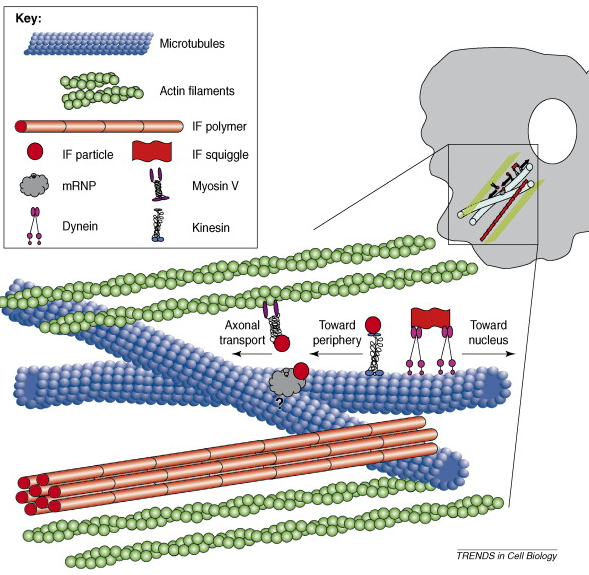
| Intermediate filaments are broadly discussed in Cytoskeleton Components in Cognition Axon and Dendrite Growth | |
| Keywords | References |
| cytoskeleton | brain physiology |
| microtubules | neurons |
| axoplasm | neuroscience |
Read more...
interpretation
Read more...
introspection
Read more...
intuition
Read more...
involuntary
Read more...
ion pump
Read more...
judgement
 A day when we all stand before the bar of God
A day when we all stand before the bar of God- A "rational" decision based on evidence
- in a court of law
- in the course of deciding how to act, where to go, and how to respond to any possible situation
Read more...
kd (kilodalton)
Read more...
kinesthesia
Read more...
knowledge
 Could it be something we have in our brain that we can remember later: something tactile like the rough of a rock or the give of a liquid? Perhaps it's visual like the cone of a volcano or the bud of a leaf? Maybe knowledge goes beyond remembered sensory experience to the abstract and symbolic. For instance, we learn that c follows b's preceded by a. Then we associate these letters with sounds and words and use words to describe our world. In data theory, knowledge is compound data that is independently meaningful.
Keywords: extra-sensory
understanding
theory
entropy
strata
short-term memory
schemata
rule base
recall
procedural memory
meta-knowledge
mamillary bodies
knowledge representation
implicit representation
hierarchical relations
episodic memory
discriminate
discern
declarative memory
common sense
causal relations
epistemology
intelligence
learning
memory
proposition
declarative knowledge
episodic knowledge
procedural knowledge
logic
inference
comprehension
References: associationism
cognition
inference
knowledge
learning
memory
taxonomy
Could it be something we have in our brain that we can remember later: something tactile like the rough of a rock or the give of a liquid? Perhaps it's visual like the cone of a volcano or the bud of a leaf? Maybe knowledge goes beyond remembered sensory experience to the abstract and symbolic. For instance, we learn that c follows b's preceded by a. Then we associate these letters with sounds and words and use words to describe our world. In data theory, knowledge is compound data that is independently meaningful.
Keywords: extra-sensory
understanding
theory
entropy
strata
short-term memory
schemata
rule base
recall
procedural memory
meta-knowledge
mamillary bodies
knowledge representation
implicit representation
hierarchical relations
episodic memory
discriminate
discern
declarative memory
common sense
causal relations
epistemology
intelligence
learning
memory
proposition
declarative knowledge
episodic knowledge
procedural knowledge
logic
inference
comprehension
References: associationism
cognition
inference
knowledge
learning
memory
taxonomy Read more...
knowledge base
Read more...
knowledge representation
Read more...
knowledge worker
Read more...
language
Read more...
Large Language Model (LLM)
Read more...
laughter
Read more...
laughter
 Another universal human response that becomes a form of communication, laughter is like crying, rolling eyes and running in the opposite direction.
It's the best medicine - and it is a conscious phenomenon.
Another universal human response that becomes a form of communication, laughter is like crying, rolling eyes and running in the opposite direction.
It's the best medicine - and it is a conscious phenomenon. Read more...
learning
Read more...
lexical
Read more...
lexicon
Read more...
limbic system
Read more...
linear discrimination
Read more...
linear discriminator
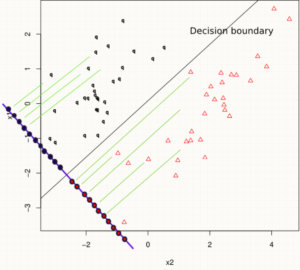 Linear discriminator functions are used to classify data. Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) is most commonly used to reduce the complexity of multi-dimensional data sets by focusing on principal attributes, features or variables and filtering out less important characteristics. This work may be the main classifier, or a pre-processing step for pattern-classification and machine learning applications. One outcome is to overlay a dataset onto a simplified space to improve the separation of objects in each class and avoid overfitting. This may also reduce computational costs.
Linear discriminator functions are used to classify data. Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) is most commonly used to reduce the complexity of multi-dimensional data sets by focusing on principal attributes, features or variables and filtering out less important characteristics. This work may be the main classifier, or a pre-processing step for pattern-classification and machine learning applications. One outcome is to overlay a dataset onto a simplified space to improve the separation of objects in each class and avoid overfitting. This may also reduce computational costs.
Read more...
linguistics
Read more...
link
Read more...
local potential
Read more...
logic
Read more...
logical form
Read more...
logorrhea
Read more...
machine learning
 A branch of cognitive computing or artificial intelligence (AI) that gives computers the ability to learn new facts, associations, and possibly processes automatically. This implies that humans may code the rules, and tell the machine where to look, but the ML takes place without real-time human participation. With supervised learning, any inferred facts, associations or processes will later be reviewed by a person to validate correctness or assign confidence values. The process-centered branch of ML focuses on developing computer systems that can teach themselves to grow or change based on new data.The content-centered branch of ML uses new facts and associations to grow or change enterprise information models.
A branch of cognitive computing or artificial intelligence (AI) that gives computers the ability to learn new facts, associations, and possibly processes automatically. This implies that humans may code the rules, and tell the machine where to look, but the ML takes place without real-time human participation. With supervised learning, any inferred facts, associations or processes will later be reviewed by a person to validate correctness or assign confidence values. The process-centered branch of ML focuses on developing computer systems that can teach themselves to grow or change based on new data.The content-centered branch of ML uses new facts and associations to grow or change enterprise information models. Read more...
mamillary bodies
Read more...
MapReduce
Read more...
Martinotti
Read more...
meaning
 Meaning is the fruit of understanding and the fuel of action. It is the contextual breaking apart and assembly of stimuli and knowledge. Meaning is neither immediate nor guaranteed, but is the quest and destination of the soul. Neither fraught with despair nor joy, meaning emerges, and all else follows. Meaning and understanding can only arise together at the junction of vision and thought in-situ. It cannot be conjured of nothing, nor can it survive in utter darkness, but thrives in the fertile soil of innate curiosity. Without meaning, there is no consciousness, no reason, no divinity, no humanity.
Keywords:
sememe semantics pragmatics noise idiom experience context expressiveness analysis
References:
chaos comprehension fuzzy logic lexicography linguistic strata natural language words/morphology
Meaning is the fruit of understanding and the fuel of action. It is the contextual breaking apart and assembly of stimuli and knowledge. Meaning is neither immediate nor guaranteed, but is the quest and destination of the soul. Neither fraught with despair nor joy, meaning emerges, and all else follows. Meaning and understanding can only arise together at the junction of vision and thought in-situ. It cannot be conjured of nothing, nor can it survive in utter darkness, but thrives in the fertile soil of innate curiosity. Without meaning, there is no consciousness, no reason, no divinity, no humanity.
Keywords:
sememe semantics pragmatics noise idiom experience context expressiveness analysis
References:
chaos comprehension fuzzy logic lexicography linguistic strata natural language words/morphology Read more...
meaningful
Read more...
mechanical brain
Read more...
medulla
Read more...
memory
Read more...
meta-knowledge
Read more...
metabolism
Read more...
metadata
 Information about data: metadata describes characteristics of the associated data that may be useful to those who seek to find or understand it:
Information about data: metadata describes characteristics of the associated data that may be useful to those who seek to find or understand it:
- Descriptive metadata tells about the content of the data and it's place in the data universe
- Lineage metadata tells where it came from and/or how it was derived
- Governance metadata tells about its sources of record and, in an organization, who is responsible for it
Read more...
metadata management
 A set of formal (stronger) or informal (weaker) processes for creating and maintaining data about content or knowledge. Metadata can describe key characteristics, such as topic, author, freshness and sensitivity of an organization's structured and unstructured information assets. Metadata can be embedded in the content, such as tagging in web pages, or held separately, such as ontologies that point to databases and files by URI or URL. The metadata can be used by systems needing the information to improve protection, integration, access, collaboration and sharing, linking, analysis, maintenance and retention. Data about content is needed for many cognitive computing processes.
A set of formal (stronger) or informal (weaker) processes for creating and maintaining data about content or knowledge. Metadata can describe key characteristics, such as topic, author, freshness and sensitivity of an organization's structured and unstructured information assets. Metadata can be embedded in the content, such as tagging in web pages, or held separately, such as ontologies that point to databases and files by URI or URL. The metadata can be used by systems needing the information to improve protection, integration, access, collaboration and sharing, linking, analysis, maintenance and retention. Data about content is needed for many cognitive computing processes. Read more...
metaphor
Read more...
metencephalon
Read more...
methodology
Read more...
metonymy
 Metonymy s a form of speech that uses an individual or an attribute as a proxy for a larger object, group or class. Examples include John Doe for an unnamed person (typically male - Jane Doe for female), oval office for the US Presidency, suit for business executive, or the track for horse racing. Metonymy is broader than synecdoche, which is strictly using a part to describe the whole. Metonymy and synecdoche both twist context in ways that only the broader context of the surrounding language can help a person (or machine) discern the true intent of the speaker or writer.
synecdoche
Metonymy s a form of speech that uses an individual or an attribute as a proxy for a larger object, group or class. Examples include John Doe for an unnamed person (typically male - Jane Doe for female), oval office for the US Presidency, suit for business executive, or the track for horse racing. Metonymy is broader than synecdoche, which is strictly using a part to describe the whole. Metonymy and synecdoche both twist context in ways that only the broader context of the surrounding language can help a person (or machine) discern the true intent of the speaker or writer.
synecdoche Read more...
microservices
- Are easily deployed.
- Require less production time.
- Can scale quickly.
- Can be reused among different projects.
- Work well with containers, such as Docker.
- Complement cloud activities."
Read more...
microtubules
Read more...
MIMD
Read more...
mind
Read more...
MIPUS
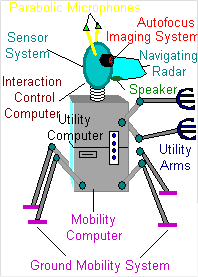 Mobile Interactive Personal Utility System. MIPUS is a household android whose main domestic tasks include clearing the dinner table and washing the dishes. He is a personable robot and very introspective; in fact, you might say he is a true synthetic life form, if such a thing is possible.
Keywords: robot
robotics
android
ALife
chaos
References: AI programming
cybernetics
ethics
genetics
neural networks
science fiction
MIPUS the Robot Assistant
MIPUS and Association Neurons
Neural Conceptual Dependency
Modeling Non-Random Synaptic Links
The Fourth Dimension
Weight Control for Knowledge
Mobile Interactive Personal Utility System. MIPUS is a household android whose main domestic tasks include clearing the dinner table and washing the dishes. He is a personable robot and very introspective; in fact, you might say he is a true synthetic life form, if such a thing is possible.
Keywords: robot
robotics
android
ALife
chaos
References: AI programming
cybernetics
ethics
genetics
neural networks
science fiction
MIPUS the Robot Assistant
MIPUS and Association Neurons
Neural Conceptual Dependency
Modeling Non-Random Synaptic Links
The Fourth Dimension
Weight Control for Knowledge
Read more...
mitochondrion
Read more...
mitosis
Read more...
model base
Read more...
modeling
Read more...
modularity
Read more...
modus ponens
Read more...
modus tollens
Read more...
morpheme
Read more...
morphology
Read more...
mossy fibers
Read more...
MT
Read more...
multi-valued logic
Read more...
munge
- to manipulate (raw data), especially to convert (data) from one format to another, or
- as a derogatory term meaning to poorly or tortuously transform disparate bits of information, or
- to completely recode a routine, data structure or program.
Read more...
myelin
Read more...
natural language
Read more...
Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
 Understanding is the ability to extract meaning. Natural language means one of thousands of symbol systems used by humans to communicate vocally and verbally. Once a word is in the wild it can't be withdrawn. But the creation of speech or writing doesn't guarantee understanding. Understanding is based on an informal agreement between the speaker/writer and the hearer/reader that the symbols in the shared language have specific definitions, and that specific grammatical patterns of phrases and sentences used to express intent and fact enable mutual empathetic collaboration. Even within a single language, different groups divided by age and gender interpret the same words and phrases differently. But as wisdom increases, people become better able to bridge those gaps in understanding. Computers, on the other hand, have never exhibited the ability to understand human intent nor to empathize. Thus, NLU in computers has not yet been achieved at any significant scale. Natural Language Processing or NLP, on the other hand, including basic grammatical analysis and phrase matching is in broad and effective use today January 2020.
Understanding is the ability to extract meaning. Natural language means one of thousands of symbol systems used by humans to communicate vocally and verbally. Once a word is in the wild it can't be withdrawn. But the creation of speech or writing doesn't guarantee understanding. Understanding is based on an informal agreement between the speaker/writer and the hearer/reader that the symbols in the shared language have specific definitions, and that specific grammatical patterns of phrases and sentences used to express intent and fact enable mutual empathetic collaboration. Even within a single language, different groups divided by age and gender interpret the same words and phrases differently. But as wisdom increases, people become better able to bridge those gaps in understanding. Computers, on the other hand, have never exhibited the ability to understand human intent nor to empathize. Thus, NLU in computers has not yet been achieved at any significant scale. Natural Language Processing or NLP, on the other hand, including basic grammatical analysis and phrase matching is in broad and effective use today January 2020. Read more...
nerve
Read more...
nerve fiber
Read more...
neural network
Read more...
neurite
Read more...
neuroanatomy
Read more...
neurocomputing
Read more...
neurode
Read more...
neuroglia
Read more...
neurogliaform
Read more...
neuromorphism
Read more...
Neuron
Read more...
NeuroPedia
Read more...
neurotransmitter
Read more...
NLP
 Natural Language Processing: using automated devices and software to do something useful with human words, phrases, sentences and more. Today there are many branches of NLP: automated translation, summarization, smart search and question answering. We are interested in going beyond basic NLP to achieve NLU and automated dialog.
Natural Language Processing: using automated devices and software to do something useful with human words, phrases, sentences and more. Today there are many branches of NLP: automated translation, summarization, smart search and question answering. We are interested in going beyond basic NLP to achieve NLU and automated dialog. Read more...
node
Read more...
noise
Read more...
non-determinism
Read more...
noosphere
Read more...
norepinephrine
Read more...
normalization
 A process used in modeling data, especially in relational databases, to minimize redundancy. Data normalization techniques can save space and improve data quality by simplifying changes to data. See Holowczak's tutorial on how to do it, and Margaret Rouse on what it is. Relational database normalization relies on Primary and foreign keys that link tables together in one-to-one or one-to-many relationships.
A process used in modeling data, especially in relational databases, to minimize redundancy. Data normalization techniques can save space and improve data quality by simplifying changes to data. See Holowczak's tutorial on how to do it, and Margaret Rouse on what it is. Relational database normalization relies on Primary and foreign keys that link tables together in one-to-one or one-to-many relationships.
First normal form (1NF) is a minimal level of normalization in which the database:
- contains any number two-dimensional tables with rows and columns named to represent the core object;
- each table's columns contain data on the attributes of the core object and the column names usually name the attribute;
- each row or record in each table represents a unique instance of the core object or attribute and must contain at least one value different from any other row (no duplicate rows are allowed);
- All entries in any column must be of the data type (date fields must contain valid dates and amount fields must contain valid numbers).
Second normal form (2NF) is an intermediate level of normalization in which each column in a table that is not a determiner of the contents of another column, must itself be a function of the other columns in the table. For example, in a "Purchases" table with columns containing "Customer ID", "Product", and "Price", the price would be a function of the customer ID and the specific product and may be derived from a separate "Prices" table.
Third normal form (3NF) is the defacto standard for transactional database modeling (reporting databases are often "denormalized"). 3NF states that all columns in a table not dependent on the primary key should be removed from the table, and placed in a separate table or eliminated. Another way of putting this is that only foreign key columns should be used to reference another table, and no other columns from the parent table should exist in the referenced table.
Read more...
object
Read more...
object-oriented
Read more...
objective
Read more...
ODBMS
Read more...
olfactory
Read more...
oligodendrocyte
Read more...
ontology
Read more...
OOPS
Read more...
Open Web vs. Deep Web
Read more...
organelle
Read more...
organism
Read more...
output
Read more...
overloading
 Some object-oriented programming languages permit reuse of the same function name to perform different functions in different contexts. This polymorphism mirrors polysemy which creates ambiguity in human languages. Function overloading or method overloading, found in programming languages such as Ada, C++, C#, Delphi, D, Java, and Swift, allows creating more than one method with the same name that differ from each other in the type of the input and the output of the function. In operator overloading, or ad hoc polymorphism, different operators have different implementations depending on their arguments. In either case, programmers are required to keep these things straight in their minds and documentation to ensure proper functioning code.
Some object-oriented programming languages permit reuse of the same function name to perform different functions in different contexts. This polymorphism mirrors polysemy which creates ambiguity in human languages. Function overloading or method overloading, found in programming languages such as Ada, C++, C#, Delphi, D, Java, and Swift, allows creating more than one method with the same name that differ from each other in the type of the input and the output of the function. In operator overloading, or ad hoc polymorphism, different operators have different implementations depending on their arguments. In either case, programmers are required to keep these things straight in their minds and documentation to ensure proper functioning code. Read more...
overshoot
Read more...
OWL
Read more...
paleo-cortex
Read more...
paradigm
Read more...
paradox
Read more...
parallel computing
Read more...
parasympathetic
Read more...
parsing
Read more...
pathology
Read more...
pattern
Read more...
perception
Read more...
perceptron
Read more...
peripheral nervous system
Read more...
permeability
Read more...
personality
Read more...
phoneme
Read more...
phonetics
The analytical science of categorizing speech sounds, their production in humans and mechanical contraptions, and their representation in written symbols.
Read more...
phrase
 A a sequential group of two or more spoken or written words that form part of a sentence, impacting the interpretation of the surrounding language
A a sequential group of two or more spoken or written words that form part of a sentence, impacting the interpretation of the surrounding language- An idiom with commonly understood meaning and usage
- A complete sentence with only a single phrase
- A syntactic structure such as: "a noun phrase composed of determiners, adjectives, subordinate noun phrases and/or prepositional phrases"
Read more...
phrenology
Read more...
physiology
Read more...
polymorphism
Read more...
polysemy
Read more...
pons
Read more...
possibility
Read more...
possible
Read more...
pragmatics
Read more...
prediction
Read more...
premise
Read more...
probability
Read more...
problem
Read more...
procedural knowledge
Read more...
procedural memory
Read more...
process
Read more...
production system
Read more...
program
 A preestablished process for doing something (the twelve-step program)
A preestablished process for doing something (the twelve-step program)- The act of writing instructions for a computer
- A set of instructions for a computer or a computer application
- A large, deep hole into which a government can dump money indiscriminately
- A show on the television
- A regimen
-
a planned series of future events, items, or performances. "a weekly program of films"
-
a presentation or item on radio or television, especially one broadcast regularly between stated times. "a nature program"
synonyms: broadcast, production, show, presentation, transmission, performance, telecast "a television program" -
dated: a radio or television service or station providing a regular succession of programs on a particular frequency; a channel.
-
-
a series of coded software instructions to control the operation of a computer or other machine.
-
provide (a computer or other machine) with coded instructions for the automatic performance of a particular task. "it is a simple matter to program the computer to recognize such symbols"
-
write computer programs. "I've programmed for 25 years and have used many languages"
-
input (instructions for the automatic performance of a task) into a computer or other machine. verb: programme; 3rd person present: programmes "simply program in your desired volume level"
-
cause (a person or animal) to behave in a predetermined way. "all members of a particular species are programmed to build nests in the same way"
-
Read more...
programming
 The art of translating human thought patterns into automated computer code. I didn't say it was useful. Much of it is not. But the stuff that is can be pretty amazing.
"Rather than increasing the number of kids who can crank out thousands of lines of JavaScript, we first need to boost the number who understand what code can do. As the cities that have hosted Code for America teams will tell you, the greatest contribution the young programmers bring isn't the software they write. It's the way they think. It's a principle called "computational thinking," and knowing all of the Java syntax in the world won't help if you can't think of good ways to apply it." (Mother Jones)
The art of translating human thought patterns into automated computer code. I didn't say it was useful. Much of it is not. But the stuff that is can be pretty amazing.
"Rather than increasing the number of kids who can crank out thousands of lines of JavaScript, we first need to boost the number who understand what code can do. As the cities that have hosted Code for America teams will tell you, the greatest contribution the young programmers bring isn't the software they write. It's the way they think. It's a principle called "computational thinking," and knowing all of the Java syntax in the world won't help if you can't think of good ways to apply it." (Mother Jones)
Read more...
programming language
 A formal language with its own syntax, reserved words (vocabulary) and tools for interpreting or compiling, that allows programmers to author a set of instructions that can be used to accept input, perform processes, and deliver various kinds of output. High level Programming languages are more readable and easier to compose, like human language, and low level languages like assembler and Op Code are less human readable, but great for folks made of highly conductive metals and silicon. The code that specifies the algorithms written in the languages can be interpreted or compiled into executable instructions for a computer.
A formal language with its own syntax, reserved words (vocabulary) and tools for interpreting or compiling, that allows programmers to author a set of instructions that can be used to accept input, perform processes, and deliver various kinds of output. High level Programming languages are more readable and easier to compose, like human language, and low level languages like assembler and Op Code are less human readable, but great for folks made of highly conductive metals and silicon. The code that specifies the algorithms written in the languages can be interpreted or compiled into executable instructions for a computer. Read more...
property
Read more...
proposition
Read more...
psyche
Read more...
psychology
Read more...
psychosis
Read more...
pump
Read more...
Purkinje
Read more...
pyramidal cells
Read more...
qualitative insight
 Unlike quantitative metrics and numerical performance indicators, qualitative answers to "why" and "how" are described in natural language, often in extended narrative text. Its sources are often social media, surveys, face-to-face interviews (dialog) and focus group transcripts. Manually assembling qualitative data to derive insight can be more difficult than quantitative data. This is why cognitive computing with natural language processing capabilities are needed to automate advanced prediction and prescription.
Unlike quantitative metrics and numerical performance indicators, qualitative answers to "why" and "how" are described in natural language, often in extended narrative text. Its sources are often social media, surveys, face-to-face interviews (dialog) and focus group transcripts. Manually assembling qualitative data to derive insight can be more difficult than quantitative data. This is why cognitive computing with natural language processing capabilities are needed to automate advanced prediction and prescription. Read more...
quantal release
Read more...
quantifiers
Read more...
quantitative insight
Read more...
RAM
Read more...
random
 Something that is devoid of a regular pattern. In the mathematical definition, it is random because we don't yet understand the laws or formulas that govern it. In other definitions, it is due to its immunity to any law which would force it into a repeating sequence that would constitute a pattern. The existence of the lawless form of randomness is purely theoretical since there is no way to prove that anything is infinitely irregular or unpredictable. Small-scale quasi-randomness (as opposed to pure randomness) is a useful tool, particularly in game theory. Does the Copenhagen Interpretation prove that there is such a thing as randomness?
Something that is devoid of a regular pattern. In the mathematical definition, it is random because we don't yet understand the laws or formulas that govern it. In other definitions, it is due to its immunity to any law which would force it into a repeating sequence that would constitute a pattern. The existence of the lawless form of randomness is purely theoretical since there is no way to prove that anything is infinitely irregular or unpredictable. Small-scale quasi-randomness (as opposed to pure randomness) is a useful tool, particularly in game theory. Does the Copenhagen Interpretation prove that there is such a thing as randomness?
| Definitions | References |
| self-similarity fractalchaos | |
| continuum probabilityinference | |
| stochastic chaoslogic | |
| dead man's hand | probability |
Read more...
range
Read more...
Ranvier, nodes of
Read more...
RAS
Read more...
RDF - Resource Description Framework
Read more...
reason
Read more...
reasoning
Read more...
recall
Read more...
receptive field
Read more...
recognition
Read more...
recursive
Read more...
reflex
Read more...
register
AX, BX, CX, DX, SI, DI, BP, and SP. The least significant 8 bits of the first four of these registers are accessible via the AL, BL, CL, and DL in all execution modes. In 64-bit mode, the least significant 8 bits of the other four of these registers are also accessible; these are named SIL, DIL, SPL, and BPL. The most significant 8 bits of the first four 16-bit registers are also available, although there are some restrictions on when they can be used in 64-bit mode; these are named AH, BH, CH, and DH.
The 80386 extended these registers to 32 bits while retaining all of the 16-bit and 8-bit names that were available in 16-bit mode. The new extended registers are denoted by adding a E prefix; thus the core eight 32-bit registers are named EAX, EBX, ECX, EDX, ESI, EDI, EBP, and ESP. The original 8-bit and 16-bit register names map into the least significant portion of the 32-bit registers.
64-bit long mode further extended these registers to 64 bits in size by adding a R prefix to the 16-bit name; thus the base eight 64-bit registers are named RAX, RBX, etc. Long mode also added eight extra registers named numerically r8 through r15. The least significant 32 bits of these registers are available via a d suffix (r8d through r15d), the least significant 16 bits via a w suffix (r8w through r15w), and the least significant 8 bits via a b suffix (r8b through r15b).
The figure below summarizes the full 64-bit x86 general purpose register set.
Read more...
regular
Read more...
relation
Read more...
relay
Read more...
representation
Read more...
response
Read more...
Rete algorithm
Read more...
RISC
Read more...
RNA
Read more...
robot
Read more...
robotics
Read more...
robust
Read more...
rule
Read more...
rule base
Read more...
sample space
Read more...
schemata
Read more...
Schwann cell
Read more...
search
Read more...
segmentation
Read more...
self
Read more...
self-similarity
Read more...
semantic network
Read more...
semantic tagging
 Then came Search Engine Optimization (SEO) in which the tools provide tagging which is separate from the document but still bound to the page using tools such as PHP or derivatives WordPress or Drupal. Finally, the loosely coupled strategy of using ontologies to perform the tagging made it possible to have completely separate processes for managing metadata and managing the content. This is especially valuable for tagging material you want to leave as is, such as a Shakespeare play or the Bible, a recorded Boston Pops concert, or a digital image of an impressionist painting or MRI of your heart. The tag lives separately and points to the associated content using a URI or URL.
Then came Search Engine Optimization (SEO) in which the tools provide tagging which is separate from the document but still bound to the page using tools such as PHP or derivatives WordPress or Drupal. Finally, the loosely coupled strategy of using ontologies to perform the tagging made it possible to have completely separate processes for managing metadata and managing the content. This is especially valuable for tagging material you want to leave as is, such as a Shakespeare play or the Bible, a recorded Boston Pops concert, or a digital image of an impressionist painting or MRI of your heart. The tag lives separately and points to the associated content using a URI or URL. Read more...
semantics
 I define semantics from a business perspective as "technology formalisms that provide structured representations of meaning and context to add business value to automated processes" that formerly or currently require human interpretation to establish such connections.
Other definitions include:
I define semantics from a business perspective as "technology formalisms that provide structured representations of meaning and context to add business value to automated processes" that formerly or currently require human interpretation to establish such connections.
Other definitions include:
- The study of meaning and roles in words and sentences.
- Semantic constraints tell us what roles words can and cannot play. Some roles are AGENT, INSTRUMENT, OBJECT, and ACTION. To be an action, a word or phrase must be a verb. Agents and objects are nominal.
- An argument that relies on word meanings in isolation without capturing the broader context
| Keywords | References |
| sememe | comprehension |
| pragmatics | context |
| MT | information/entropy |
| syntax | linguistic strata |
| language | natural language |
| linguistics | semantics |
| meaningful | syntax |
| expressiveness | words/morphology |
Read more...
sememe
Read more...
semiotics
Read more...
sense
Read more...
sensory
Read more...
sensory transduction
Read more...
sentence
Read more...
sentient
Read more...
Service-Oriented Architecture
Read more...
services
Read more...
short-term memory
Read more...
SIMD
Read more...
slicing and dicing
 A process often used in kitchens involving knives or small electric appliances to reduce the size of edibles
A process often used in kitchens involving knives or small electric appliances to reduce the size of edibles- A process used in Business Intelligence (BI) and analytics to change the view, add or remove details, or rearrange the data to make it easier for humans to analyze. Sometimes considered synonymous with filtering and sorting.
Read more...
SME - subject matter expert
Read more...
SOA
Read more...
software
Read more...
soma
Read more...
somatosensory cortex
Read more...
space
Read more...
SPARQL
Read more...
specialization
Read more...
spike
Read more...
spinal cord
Read more...
SQL (Structured Query Language)
Read more...
standard deviation
Read more...
state space
Read more...
statistical analysis
Read more...
stellate cells
Read more...
stimulus
Read more...
stochastic
Read more...
strata
Read more...
string
 A theory about how the universe works (see String Theory or Super String Theory)
A theory about how the universe works (see String Theory or Super String Theory)- Something the cat likes to play with
- A sequence of symbols that are intended to represent meaning in one dimension
Read more...
structure
Read more...
subconscious
Read more...
subjective
Read more...
subliminal
Read more...
sulcus
Read more...
support vector machine
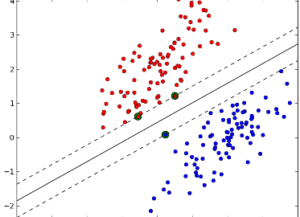 A Support Vector Machine (SVM) is a classifier formally characterized by a hyperplane separating the data elements to classify. For a set of labeled training data, this supervised learning algorithm outputs an optimal hyperplane to categorize new samples through classification and regression analyses.
For a good tutorial, formulas and sample code, see OpenCV
A Support Vector Machine (SVM) is a classifier formally characterized by a hyperplane separating the data elements to classify. For a set of labeled training data, this supervised learning algorithm outputs an optimal hyperplane to categorize new samples through classification and regression analyses.
For a good tutorial, formulas and sample code, see OpenCV Read more...
survival
Read more...
syllogism
Read more...
symbol
Read more...
symbolic logic
Read more...
symmetry
Read more...
synapse
Read more...
synaptic vesicle
Read more...
syncretism
Read more...
synecdoche
 Synecdoche is a form of speech in which you use a part to refer to its whole or vice-versa. Here are some good examples from World Wide Words: "You use this when you speak of a part of something but mean the whole thing. When Patrick O’Brian has Captain Jack Aubrey tell his first lieutenant to “let the hands go to dinner” he’s employing synecdoche, because he’s using a part (the hand) for the whole man. You can also reverse the whole and the part, so using a word for something when you only mean part of it. This often comes up in sport: a commentator might say that “The West Indies has lost to England” when he means that the West Indian team has lost to the English one. America is often used as synecdoche in this second sense, as the word refers to the whole continent but is frequently applied to a part of it, the USA."
Synecdoche is narrower than metonymy, which may use an individual or an attribute to describe an object, group or class. Metonymy and synecdoche both twist context in ways that only the broader context of the surrounding language can help a person (or machine) discern the true intent of the speaker or writer.
metonymy
Synecdoche is a form of speech in which you use a part to refer to its whole or vice-versa. Here are some good examples from World Wide Words: "You use this when you speak of a part of something but mean the whole thing. When Patrick O’Brian has Captain Jack Aubrey tell his first lieutenant to “let the hands go to dinner” he’s employing synecdoche, because he’s using a part (the hand) for the whole man. You can also reverse the whole and the part, so using a word for something when you only mean part of it. This often comes up in sport: a commentator might say that “The West Indies has lost to England” when he means that the West Indian team has lost to the English one. America is often used as synecdoche in this second sense, as the word refers to the whole continent but is frequently applied to a part of it, the USA."
Synecdoche is narrower than metonymy, which may use an individual or an attribute to describe an object, group or class. Metonymy and synecdoche both twist context in ways that only the broader context of the surrounding language can help a person (or machine) discern the true intent of the speaker or writer.
metonymy
Read more...
syntax
Read more...
synthesis
Read more...
systaltic array
Read more...
systaltic array
 A systaltic array is a connected set of computational nodes that support bi-directional (systolic and diastolic) information flow. Neural networks are one-directional models for processing and sometimes the opposite (backpropagation) for learning. As shown in the illustration at right, a systaltic process model may use process flow scripts or forward chaining inference in parallel with independent knowledge search and retrieval to solve complex problems.
A systaltic array is a connected set of computational nodes that support bi-directional (systolic and diastolic) information flow. Neural networks are one-directional models for processing and sometimes the opposite (backpropagation) for learning. As shown in the illustration at right, a systaltic process model may use process flow scripts or forward chaining inference in parallel with independent knowledge search and retrieval to solve complex problems. Read more...
systolic array
Read more...
tactile agnosia
Read more...
taxonomy
 The science of categorizing or classifying things hierarchically. Object-oriented programming techniques use inheritance from classes to subclasses to imitate the fundamentally taxonomical structure of information in the real world and in the mind. Taxonomies are a key component of generalization, a basic human cognitive activity.
Keywords: hierarchical relations
categorize
class
inheritance
generalization
structure
cognition
form
References:
associationism
cognition
inference
knowledge
The science of categorizing or classifying things hierarchically. Object-oriented programming techniques use inheritance from classes to subclasses to imitate the fundamentally taxonomical structure of information in the real world and in the mind. Taxonomies are a key component of generalization, a basic human cognitive activity.
Keywords: hierarchical relations
categorize
class
inheritance
generalization
structure
cognition
form
References:
associationism
cognition
inference
knowledge Read more...
telecosm
Read more...
thalamus
Read more...
thalamus
 The thalamus is a small structure within the brain located just above the brain stem between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain and has extensive nerve connections to both. The main function of the thalamus is to relay motor and sensory signals to the cerebral cortex. It also regulates sleep, alertness and wakefulness (Dr Ananya Mandal, MD on News.medical.net)
The thalamus is a small structure within the brain located just above the brain stem between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain and has extensive nerve connections to both. The main function of the thalamus is to relay motor and sensory signals to the cerebral cortex. It also regulates sleep, alertness and wakefulness (Dr Ananya Mandal, MD on News.medical.net) Read more...
theory
Read more...
think
Read more...
thought
Read more...
threshold
Read more...
time
Read more...
tools
Read more...
translation
Read more...
uncertainty
Read more...
understanding
Read more...
Unstructured Content
Read more...
voice recognition
 I recognize my wife's voice on the phone, but this is way different. This voice recognition is a misnomer for computationally recognizing words when spoken (voiced) into a microphone. Speech to text or STT may be a better expression for this conversion that translates sound waves into patterns that can be matched with words and phrases to tell a digital device what a person just said (i.e. "read your lips"). This is also completely different from language understanding, which begins with the words and tries to determine what prompted you to say something, or your intent (i.e. "read your mind").
I recognize my wife's voice on the phone, but this is way different. This voice recognition is a misnomer for computationally recognizing words when spoken (voiced) into a microphone. Speech to text or STT may be a better expression for this conversion that translates sound waves into patterns that can be matched with words and phrases to tell a digital device what a person just said (i.e. "read your lips"). This is also completely different from language understanding, which begins with the words and tries to determine what prompted you to say something, or your intent (i.e. "read your mind"). Read more...
volition
Read more...
weight
Read more...
Wernicke's area
Read more...
white matter
Read more...
word
Read more...
workflow
Read more...
Yorrick
 Yorrick is the name of a fictional human being I have invented to illustrate the knowledge acquisition and language acquisition processes. See the following posts:
Yorrick: Seeds of Knowledge
Remember Yorrick
Conceptual Paradigms
From Concept to Communication
Knowing About Agents and Instruments
Yorrick is the name of a fictional human being I have invented to illustrate the knowledge acquisition and language acquisition processes. See the following posts:
Yorrick: Seeds of Knowledge
Remember Yorrick
Conceptual Paradigms
From Concept to Communication
Knowing About Agents and Instruments Read more...
zygote
Read more...